Hypothyroidism, also called hypothyroidism, is when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones to meet the body’s needs. The thyroid gland and its hormones play many important roles in body function and metabolism. Read ahead to learn more about hypothyroidism and hypothyroidism.
What is hypothyroidism?
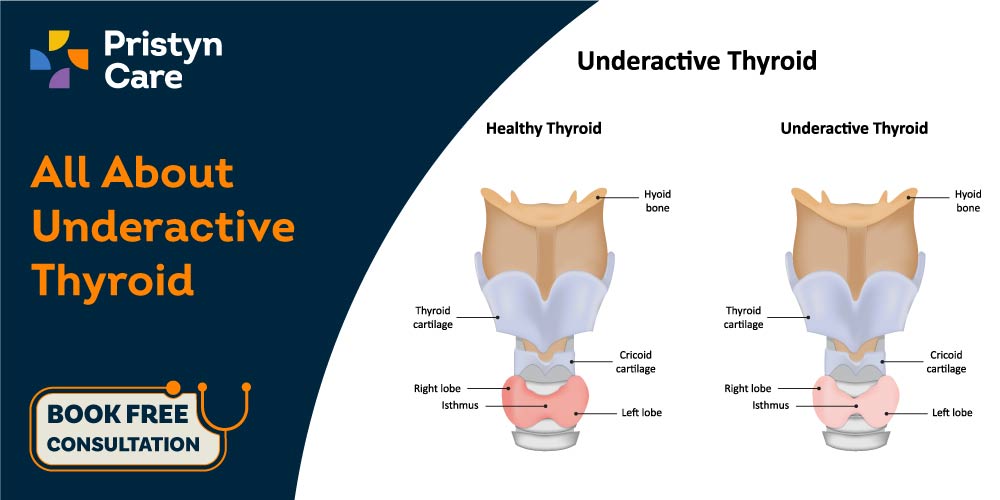
Hypothyroidism or hypothyroidism is a very common condition, especially among women. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ in the front of the neck. It forms hormones that directly affect the body’s metabolism, heart rate, energy production, etc.
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism are:
- Malaise
- weight gain and high cholesterol
- hard to bear the cold
- muscle and joint pain
- dry skin
- thinning hair
- slow heart rate
- depression
These symptoms progress so slowly that they are barely noticeable in the early stages. This is why the condition can go undiagnosed for months, sometimes years.
Who Can Have Hypothyroidism?
but thyroid problems Hypothyroidism can occur in both men and women of any age, but in general, it is more common in women and people over the age of 60. Other conditions that can lead to hypothyroidism are:
- have another thyroid problem, such as a goiter
- have been treated for hyperthyroidism with surgery or radioactive iodine
- have radiation therapy, especially to the neck, thyroid, or chest
- you have a family history of thyroid disease
- pregnancy
- Turner syndrome
- Health problems such as celiac disease, Sjögren’s syndrome, pernicious anemia, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus
There are many health problems associated with hypothyroidism during pregnancy It is especially dangerous at this time, as it can affect both mother and baby.
What are the complications of hypothyroidism?
Low thyroid hormones contribute to cholesterol and can cause many other overall health problems. Some common complications of untreated hypothyroidism include:
- Goiter: Continued stimulation of thyroid hormones can cause the thyroid gland to enlarge, known as goiter formation. While not uncomfortable, it can affect appearance and eventually make breathing and swallowing difficult. .
- heart problems: Because thyroid hormones directly affect heart rate and cholesterol levels, underactive thyroid glands increase the risk of heart disease and heart failure.
- Mental health issues: Depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues are common in patients with hypothyroidism.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Uncontrolled thyroid hormone levels over a long period of time can damage the peripheral nerves present in the arms and legs, ultimately resulting in pain, numbness, and tingling in the affected areas.
- Myxedema: A severely underactive thyroid can also lead to myxedema coma, an extreme form of hypothyroidism that can lead to severely impaired and potentially fatal thyroid function. Myxomatous coma should be treated as soon as it occurs. It is usually caused by sedatives, infections, and other stresses on the body.
- infertility: Low thyroid levels interfere with ovulation and impair the body’s fertility. However, most can be countered with proper hormone management.
- Birth defects: Women with severely underactive thyroids are often at increased risk of giving birth to defective babies compared to healthy mothers. Infants with untreated hypothyroidism are also at increased risk of developing physical and psychological problems.
What Causes Hypothyroidism?
Common causes of hypothyroidism and hypothyroidism include:
It is an autoimmune disease and the most common cause of hypothyroidism. In this condition, the immune system begins to attack the thyroid gland, causing inflammation of the thyroid gland and decreased production of thyroid hormones.
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland that leads to leakage of thyroid hormones. Initially it leads to thyrotoxicosis, a rapid rise in thyroid levels in the blood, but over time thyroid levels can become dangerously low. It can even lead to hypofunction. It is also common among women who have recently given birth.
- congenital hypothyroidism
Early treatment is important for all such problems because congenital hypothyroidism is present at birth and can lead to intellectual disability and failure to thrive. To avoid it, they are tested for thyroid problems at birth.
- Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland
Thyroidectomy, or removal of the thyroid gland, is also a major cause of hypothyroidism. Removal of the entire thyroid always results in hypothyroidism. It is usually done for problems such as hyperthyroidism, large goiters, thyroid nodules, and cancer.
- Radiation therapy of the thyroid
Radioactive iodine is a very common conservative treatment for hyperthyroidism, which gradually destroys the thyroid cells. Ultimately, this condition causes hypothyroidism due to excessive damage to the thyroid cells. Possibly. Radiation therapy for head and neck cancer is another way radiation can damage the thyroid.
Some medications, such as heart medications, bipolar medications, and cancer drugs, can interfere with hormone production and result in hypothyroidism. Your medication is affecting thyroid production. If so, your doctor may prescribe an alternative medicine.
Iodine is a key component of the thyroid hormone production process, and nutritional deficiencies like iodine deficiency can lead to reduced thyroid production. It is very common in
- Disorders of the pituitary or hypothalamic gland
The pituitary and hypothalamic glands produce certain hormones and enzymes that affect the function of thyroid hormones. Therefore, their disturbances can interfere with thyroid function and even lead to hypothyroidism. This is known as secondary or tertiary hypothyroidism. This is because the problem is in another gland, causing hypothyroidism as a secondary factor.
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
To diagnose hypothyroidism, doctors take a medical history and do a physical examination. The symptoms of hypothyroidism are very similar to those of a variety of health problems, so a diagnosis cannot be established based on both of these alone. Blood tests and imaging of the thyroid are needed to find the cause. Because it affects fertility and fertility, most women are tested for hypothyroidism when they start experiencing fertility problems.
How is hypothyroidism managed?
The best treatment for hypothyroidism is with hormone replacement therapy. The best hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism is with the drug levothyroxine. It is usually taken in tablet form in the early morning before meals.
Your doctor will do blood tests every 6 to 8 weeks after you start hormone replacement therapy. Adjust the dosage according to the test results. Once the results have normalized, a thyroid examination is to be performed annually.
However, too much thyroid hormone can cause serious problems such as atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis, so thyroid medications should be taken as prescribed.
In addition to medications, diet and nutrition are also important parts of thyroid treatment. Hashimoto’s disease and other autoimmune thyroid diseases are sensitive to iodine, and eating iodine-rich foods can exacerbate the problem. please.
Can hypothyroidism be prevented?
Hypothyroidism due to iodine and nutritional deficiencies can be prevented, but not autoimmune thyroid disorders. The best way to prevent the serious effects of hypothyroidism is to seek treatment as soon as possible. If you have symptoms of hypothyroidism, you should talk to your health care provider and get prompt treatment.
Foods high in iodine include eggs, dairy products, meat, poultry, seaweed, seafood, and iodized salt. Your health care provider will provide you with dietary charts and plans to help you manage your condition. Mild cases of hypothyroidism always go away over time, but as the patient’s thyroid function progresses, If it drops and hormone levels remain depressed for a long period of time, patients may develop complications for the rest of their lives.
https://www.pristyncare.com/blog/underactive-thyroid-hypothyroidism/ Hypothyroidism (Hypothyroidism) – Pristyn Care